Archive for April 2014
Reflective Post
By : AnnieAKiwiReflection
Photo credit to Ana (Me).
This course was extremely helpful and informative about
using technology in education. I was able to demonstrate my skills about
computers and websites and expand my creativity online. By writing online
journals, I was able to both express my thoughts and discuss the textbooks
content to the public. The website review assignment allowed me to evaluate and
recognize which websites to trust. The discussion board was a way for us as
students to interact with each other online and discuss topics. It gave us the opportunity
to analyze and evaluate each topic and the involvement of technology. Two projects
that enabled us to cooperate with classmates as a team was the wiki and collaborative
lesson plan. The wiki and webquest helped me “create a portfolio with samples
reflecting ways technology can support classroom management, administration,
and teaching in a K-12 classroom” (Coleman). When I was creating the wiki, I managed to create a Voki for visual and audio enhancement. The webquest gave me an
opportunity to design an internet assignment using several online resources for
middle school students. I learned how to give credit to photos and search
non-copyright photos on Google and Flickr. GPS-Caching was an outstanding way
to get the classroom involved and away from lectures. The last project, the
teacher e-portfolio, was a project where I put all of what I learned in class
into this website. It allowed me to view how I’ve developed over the semester.
The overall quality of the course was more than just about right. I learned
more things in this class than in any other class. There are no suggestions improving
this course, since what I’ve learned will be useful now and for the future. As
a future teacher, I will be able to use these skills for my students in the
classroom.
Resources:
Coleman. (n.d.). Edison State
College Syllabus. . Retrieved April 24, 2014, from
http://eme2040edison.wikispaces.com/file/view/EME%202040%20INTRO%20TO%20TECH%20FOR%20EDUC_Coleman_SP14.pdf/479780492/EME%202040%20INTRO%20TO%20TECH%20FOR%20EDUC_Coleman_SP14.pdf
Chapter 11 – Engaging Students in Performance Assessment and Reflective Learning
By : AnnieAKiwi
Focus question: How
can teachers and students use digital portfolios as tools for learning?
A teacher will be evaluated throughout their career, which
sets the context for developing a digital teaching portfolio. Digital teaching
portfolios is where teachers store a collection of educational and professional
materials in an electronic format. It allows teachers to organize a collection
of educational materials, which shows their growth and development over time. The
digital portfolio may contain Word documents, PowerPoint, videos, pictures, and
copies of paper materials.
In this class, we are creating our own portfolios where we
can store our educational materials. Once we finish it, we will be able to
provide career-related information to teaching colleagues and school administrators.
It will be a way to store activities, ideas, field experiences, summer work,
and community volunteering over time. These portfolios give us an opportunity
as future teachers to reflect on our developments.
Portfolios can be used to “connect teaching skills and
competencies to teaching or curriculum standards as way to show that new
teacher candidates are qualified to receive a license or…to remain as the
teacher-in-charge in the classroom” (Maloy,
R. W., Verock-O, R. E., Edwards, S. A., & Woolf, 2011). It enables us as
future teachers to acquire a distinguishing quality of master teachers and to
think critically and creatively. It’s a good idea to update your portfolio so
it won’t become a “celebratory scrapbook of the past,” but promote growth and
change in our minds and works. Students will be able to use to portfolios for
their personal and public piece of writing. It’s easier to store electronically
because teachers and students can take it anywhere without having to worry
about missing pages. It will also increase their confidence and technological
skills.
Tech Tool Link: Survey
and Poll Resources and Apps
In this class, we have used poll apps before with our cell
phones. Surveys and polls online are ways to generate discussions in classrooms
and conduct instructional preassessments. The article provides some websites
and apps for teachers to look up. SurveyMonkey is an online survey tool that
can be used to formulate questions and collect information. Poll Everywhere is
a texting app that is used to submit responses to questions using cell phones.
Photo credit to Wesley Fryer on Flickr.
Summary &
Connection:
This chapter examines on the role of assessment in teaching
and learning. Teachers evaluate the students learning by using assessments. Assessments
have three interrelated elements: new teacher assessment, student assessment,
and student self-assessment. Student assessment is how teachers will assess
students’ learning while new teacher assessment is how supervisors will assess
the teacher’s work. Student self-assessment is when students are active in the
evaluation of their own learning. Assessments let teachers’ know where they
need to change and what other strategies to use. Digital portfolios is a way
for teachers to see their own growth and development over time.
Students involved in their learning and assessment will
motivate them more to complete the assignment. Students have little or no
influence on curriculum topics in many classrooms. It’s an opportunity lost
when a teacher fails to give students a voice in decision-making. Students can
use digital portfolios to learn more about how to use computers and other
tools. It can also increase their confidence. This chapter also explains with
how online surveys enable students to self-reflect about their learning.
Resources:
Maloy, R. W.,
Verock-O, R. E., Edwards, S. A., & Woolf, B.P.
(2011). Transforming learning with new
technologies. (2nd ed.). Boston, MA: Pearson Education Inc.
Chapter 10 – Promoting Success for All Students through Technology
By : AnnieAKiwi
Focus question: How
can assistive technologies be incorporated into instruction to support teaching
all learners?
Assistive technology enable students to become more
independent in school and throughout their life. It allows teachers to
“differentiate instruction and pursue universal design” (Maloy, R. W., Verock-O, R. E., Edwards, S. A., & Woolf,
2011). Disabled children use assistive technologies to learn and
function more effectively. Individuals with hearing, sight, mobility, or
cognitive challenges are able to translate text and understand spoken words. AT
can be communication boards, special purpose computers, prosthetics, attachment
devices, positioning devices, screen-readers, communication software,
educational software, specialized learning materials, and curriculum aids.
Teachers need to be actively involved with the child, in addition to using
technology.
A software that displays written text from a person’s spoken
words is speech recognition. Individuals with fine motor disabilities and
dyslexia use this software. Some individuals prefer to speak than write or type
their ideas. Users need to train the system to recognize one or more major
voices by speaking into the microphone for speech recognition programs. The
software learns to recognize the individual’s speech patterns and tonal
nuances. The software provides students a new way to record their thoughts.
Although it transfers spoken words to written text, it still needs to be
revised by teacher and student.
Text reading software are available in many versions, which
enables users to “hear written text aloud by a computer” (Maloy, R. W., Verock-O, R. E., Edwards,
S. A., & Woolf, 2011). When I observed elementary classes, I noticed that
students can listen to stories on the computer. They have the story in front of
them, but they have the option of having the computer read the story to them. It’s
a wonderful tool for students who learn better through a multimodal experience that
supports decoding letters, sounds, and words by listening to text read aloud. Screen
reading software is a type of text-to-speech software. This software is like a
translator for the visual page. It has features that allows the user to know
the whereabouts and actions of the mouse. The screen reading software reads the
text that was scanned on the computer screen. Some examples include JAWS,
VoiceOver from Apple, Google Chrome, and TalkBack.
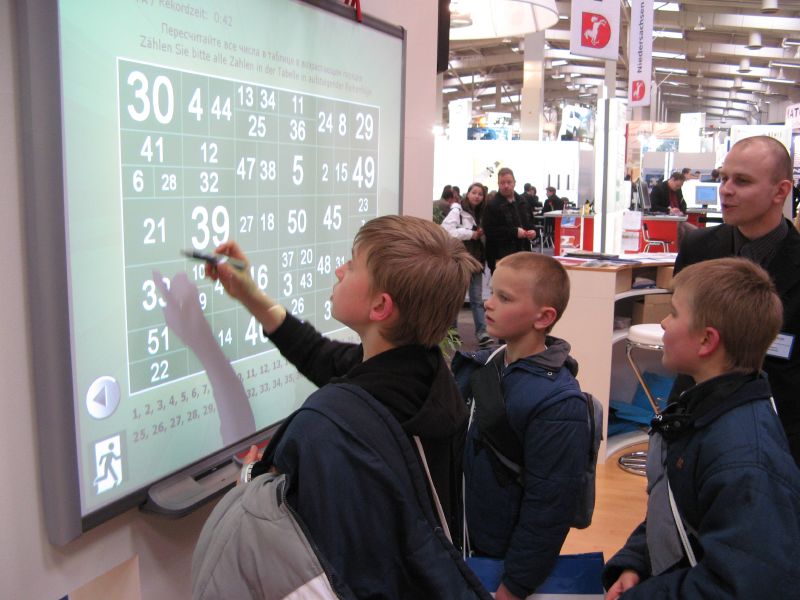
Tech Tool link: Interactive
Whiteboards
Interactive whiteboards are mounted on a wall or whiteboard.
It’s connected to a computer and a projector, which allows “teachers and
students to access a computer’s desktop directly at the board using a finger,
pen, or other touch device” (Maloy,
R. W., Verock-O, R. E., Edwards, S. A., & Woolf, 2011). Interactive
whiteboards show any material on your computer screen in large size. It creates
instructional opportunities for students as a class, groups, or individual. Teachers
can use it for visual, auditory, and hand-on learning activities.
Summary &
Connection:
This chapter explains about how teachers have opportunities
to meet the learning needs of all students through computer technologies. Diversity
students show more interest in U.S. history when they see that teachers have integrated
stories and histories of multiple peoples. Technologies such as interactive
websites, online videos, and web-based primary source materials bring names of individuals
or groups that are not mentioned in books and lesson plans.
Teachers and students are able to access resources from the
internet to explore multiple languages. These resources provide opportunities
to English speakers and students that are learning English. An example of a
helpful resource is online language translation service. Both students and
teachers can access Google Translate, which is free and available as a website
and app for smartphones and tablets. Teachers are able to translate notes,
assignments, letters to parents, and other materials for students of multiple
languages. “Technology supports diverse students and multicultural education” (Maloy, R. W., Verock-O, R. E., Edwards,
S. A., & Woolf, 2011).
The chapter further discusses about differentiated
instruction (DI) and universal design for learning (UDL). The purpose of DI and UDL is to address
the needs of diverse students with curriculum and instruction. It benefits
students with special educational needs, gifted and talented learners, or ELL
by meeting their needs and differentiating classroom activities. Teachers
create different educational experiences to meet students need called DI. UDL
is “the application of universal design principles to educational settings” (Maloy,
R. W., Verock-O, R. E., Edwards, S. A., & Woolf, 2011). In order to serve
the needs of the widest range of students, teaching and learning situations are
created. Students with disabilities use assistive technology to learn and function
in society.
Resources:
Maloy, R. W.,
Verock-O, R. E., Edwards, S. A., & Woolf, B.P.
(2011). Transforming learning with new
technologies. (2nd ed.). Boston, MA: Pearson Education Inc.